- Bài 1: Tổng quan về hệ điều hành Android
- Bài 2: Lập trình Android với Android studio
- Bài 3: Các thành phần cơ bản trong một ứng dụng Android
- Bài 4: Activity
- Bài 5: Fragment
- Bài 6: Các thành phần giao diện cơ bản trong Android
- Bài 7: Layout trong Android : Phần 1
- Bài 8: Layout trong Android : Phần 2
- Bài 9: Style và Theme trong Android
- Bài 10: Listview trong Android
- Bài 11: RecyclerView trong Android
- Bài 12: Menu trong Android
- Bài 13: Sử dụng Dialog trong Android
- Bài 14: AndroidManifest.xml Trong Android
- Bài 15: Các tài nguyên và ứng dụng cơ bản trong Android
- Bài 16: Intent trong Android
- Bài 17: Lưu trữ dữ liệu trong Android
- Bài 18: Service trong Android
- Bài 19: Content provider trong Android
- Bài 20: Broadcast Receivers trong Android
- Bài 21: SQLite trong Android
- Bài 22: Android notification
- Bài 23: Animation trong Android
- Bài 24: Android Drawables
- Bài 25: Room trong Android
- Bài 26: CursorLoader trong Android
- Bài 27: Databinding trong Android
- Bài 28: Toolbar, ActionBar trong lập trình Android
- Bài 29: AsyncTask – thread & handler trong Android
- Bài 30: Các thư viện thường dùng trong Android
- Bài 31: Tìm hiểu về MVC, MVP và MVVM
- Bài 32: AlarmManager trong Android
- Bài 33: Permission trong Android
- Bài 34: Đóng gói ứng dụng Android
Bài 13: Sử dụng Dialog trong Android - Lập trình Android cơ bản
Đăng bởi: Admin | Lượt xem: 6011 | Chuyên mục: Android
1. Giới thiệu Dialog trong Android
Dialog trong Android là một cửa sổ nhỏ dùng để nhắc người dùng đưa ra quyết định hoặc nhập thông tin.
Thỉnh thoảng trong ứng dụng của bạn, nếu bạn muốn hỏi người dùng về quyết định giữa có hoặc không để phản hồi bất kỳ hành động cụ thể nào do người dùng thực hiện, bằng cách giữ nguyên hoạt động và không thay đổi màn hình, bạn có thể sử dụng hộp thoại cảnh báo (Alert Dialog).
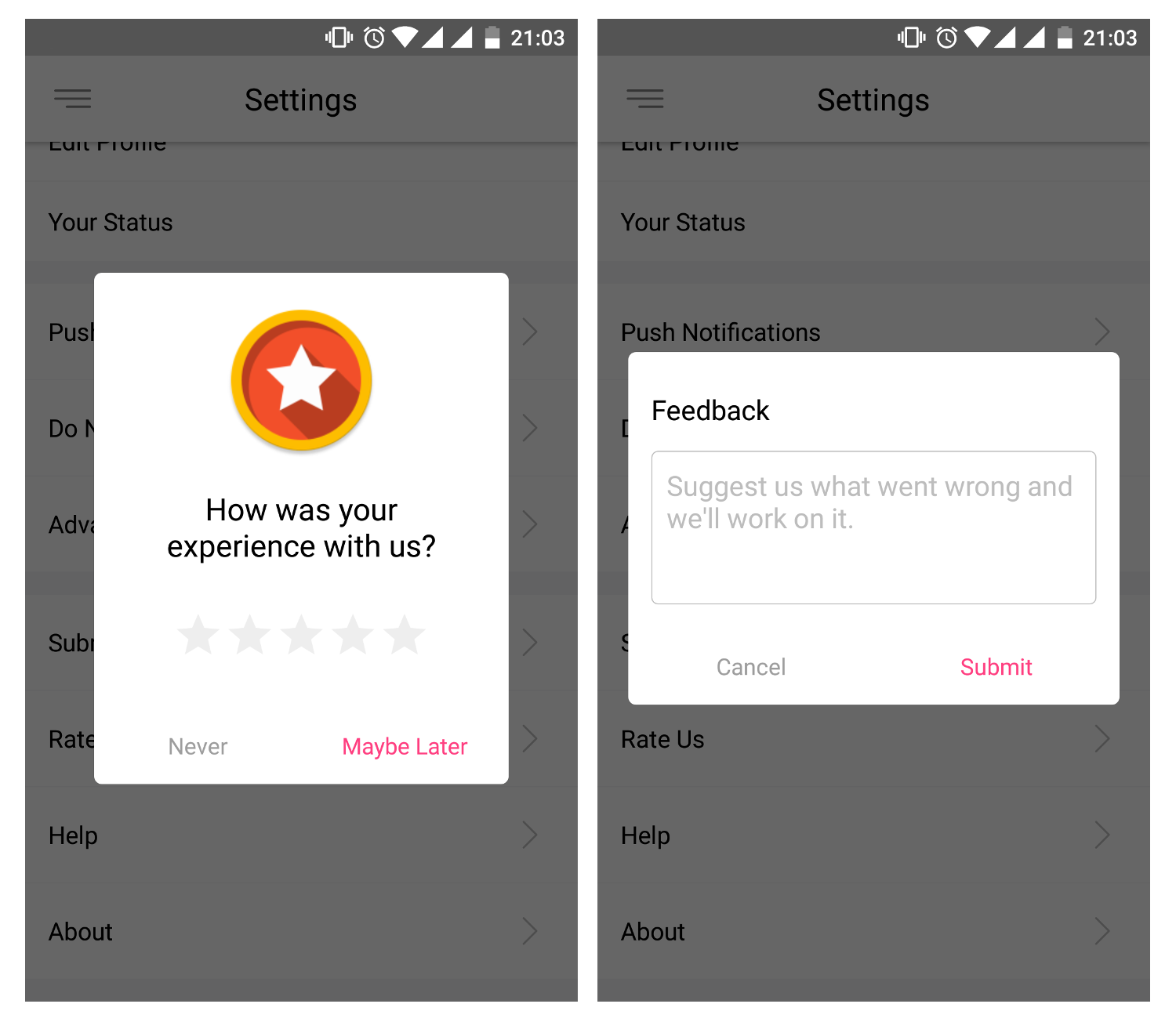
Có nhiều loại Dialog như ListDialog hay AlertDialog nhưng bạn có thể tùy chỉnh giao diện của Dialog sao cho phù hợp với ứng dụng của mình.
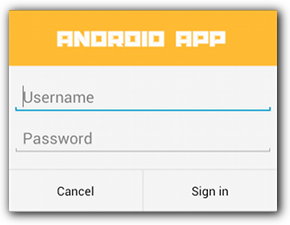
Giao diện của 1 Dialog tùy chỉnh giao diện.
2. AlertDialog
Để hiển thị hộp thoại cảnh báo (Alert Dialog), bạn cần tạo một đối tượng của AlertDialogBuilder theo câu lệnh sau:
AlertDialog.Builder b = new AlertDialog.Builder(this);Bây giờ, bạn có thể thiết lập nút đồng ý (yes) hoặc nút không đồng ý (no) bằng cách sử dụng đối tượng đã tạo ở trên.
//Nút đồng ý
b.setPositiveButton(String caption, listener);
//Nút không đồng ý
b.setNegativeButton(String caption, listener);Một số phương thức thường dùng với Alert Dialog
setIcon(Drawable icon): Phương thứ này thiết lập icon cho AlertDialog
setTitle(String title): Phương thức này thiết lập tiêu đề.
setMessage: Phương thức này thiết lập thông điệp.
Ví dụ tạo AlertDialog trong Android
//Tạo đối tượng
AlertDialog.Builder b = new AlertDialog.Builder(this);
//Thiết lập tiêu đề
b.setTitle("Xác nhận");
b.setMessage("Bạn có đồng ý thoát chương trình không?");
// Nút Ok
b.setPositiveButton("Đồng ý", new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() {
public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, int id) {
finish();
}
});
//Nút Cancel
b.setNegativeButton("Không đồng ý", new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() {
public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, int id) {
dialog.cancel();
}
});
//Tạo dialog
AlertDialog al = b.create();
//Hiển thị
al.show();2. List Dialog
Hiển thị danh sách lựa chọn trong dialog. Có 3 loại list dialog được hỗ trợ trong android bao gồm single-choice list, single-choice list (radio buttons) và multiple-choice list (checkboxes).
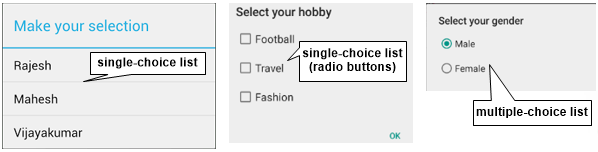
Tạo single-choice list
//Items
String[] items = {"Rajesh", "Mahesh", "Vijayakumar"};
AlertDialog.Builder b = new AlertDialog.Builder(getActivity());
//Thiết lập title
b.setTitle("Make your selection");
//Thiết lập item
b.setItems(items, new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() {
//Xử lý sự kiện
public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, int which) {
}
});
//Hiển thị dialog
b.show();Tạo single-choice list (radio buttons)
//Items
String[] datas = {"Male", "Female"};
AlertDialog.Builder b = new AlertDialog.Builder(this);
b.setSingleChoiceItems(datas, 0, new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, int which) {
}
});
b.show();Tạo multiple-choice list (checkboxes)
String[] datas = {"Football", "Travel", "Fashion"};
ArrayList al = new ArrayList();
AlertDialog.Builder b = new AlertDialog.Builder(getActivity());
b.setMultiChoiceItems(datas, null,new DialogInterface.OnMultiChoiceClickListener(){
@Override
public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, int which, boolean isChecked) {
//Nếu người dùng chọn
if (isChecked) {
//Thêm người dùng người dùng chọn vào ArrayList
al.add(datas[which]);
}
}
});
b.show();3. Custom Dialog
Custom Dialog được sử dụng rất nhiều trong các ứng dụng, ví dụ như form đăng nhập hay đăng ký chẳng hạn, các bạn rất dễ bắt gặp những dạng custom dialog như vậy.
File layout:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
>
<TextView
android:textSize="20dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:id="@+id/textView1"
android:text="vncoder.vn"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_gravity="center_horizontal"
android:layout_weight="1">
</TextView>
<Button android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:id="@+id/btnLoginDialog"
android:text="show dialog"
android:layout_gravity="center_vertical"
android:layout_height="wrap_content">
</Button>
</LinearLayout>Tạo tập tin login_dialog.xml trong layout :
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_width="300dp"
android:paddingTop="10dp">
<EditText android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:id="@+id/edtUsername"
android:layout_width="match_parent">
<requestFocus></requestFocus>
</EditText>
<EditText
android:id="@+id/edtPassword"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:inputType="textPassword"
android:layout_width="match_parent">
</EditText>
<LinearLayout android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:id="@+id/linearLayout1">
<Button android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_weight="0.5"
android:id="@+id/btnLogin"
android:text="Login">
</Button>
<Button android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_weight="0.5"
android:id="@+id/btnCancel"
android:text="Cancel">
</Button>
</LinearLayout>
</LinearLayout>Xử lý sự kiện onClick trong MainActivity:
public void onClick(View v) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
final EditText edtUserName, edtPassword;
Button btnLogin, btnCancel;
AlertDialog.Builder dialogBuilder = new AlertDialog.Builder(this);
LayoutInflater inflater = this.getLayoutInflater();
View dialogView = inflater.inflate(R.layout.login_dialog, (ViewGroup)findViewById(R.layout.activity_main));
edtUserName = (EditText) dialogView.findViewById(R.id.edtUsername);
edtPassword = (EditText) dialogView.findViewById(R.id.edtPassword);
btnLogin = (Button) dialogView.findViewById(R.id.btnLogin);
btnCancel = (Button) dialogView.findViewById(R.id.btnCancel);
btnLogin.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
if(edtUserName.getText().equals("vncoder.vn")&& edtPassword.getText().equals("hiepsiit")){
Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this, "Đăng nhập thành công", Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
finish();
}
else
Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this, "Đăng nhập không thành công", Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
}
});
btnCancel.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
finish();
}
});
dialogBuilder.setView(dialogView);
dialogBuilder.setTitle("Đăng nhập");
AlertDialog b = dialogBuilder.create();
b.show();
}
Theo dõi VnCoder trên Facebook, để cập nhật những bài viết, tin tức và khoá học mới nhất!
- Bài 1: Tổng quan về hệ điều hành Android
- Bài 2: Lập trình Android với Android studio
- Bài 3: Các thành phần cơ bản trong một ứng dụng Android
- Bài 4: Activity
- Bài 5: Fragment
- Bài 6: Các thành phần giao diện cơ bản trong Android
- Bài 7: Layout trong Android : Phần 1
- Bài 8: Layout trong Android : Phần 2
- Bài 9: Style và Theme trong Android
- Bài 10: Listview trong Android
- Bài 11: RecyclerView trong Android
- Bài 12: Menu trong Android
- Bài 13: Sử dụng Dialog trong Android
- Bài 14: AndroidManifest.xml Trong Android
- Bài 15: Các tài nguyên và ứng dụng cơ bản trong Android
- Bài 16: Intent trong Android
- Bài 17: Lưu trữ dữ liệu trong Android
- Bài 18: Service trong Android
- Bài 19: Content provider trong Android
- Bài 20: Broadcast Receivers trong Android
- Bài 21: SQLite trong Android
- Bài 22: Android notification
- Bài 23: Animation trong Android
- Bài 24: Android Drawables
- Bài 25: Room trong Android
- Bài 26: CursorLoader trong Android
- Bài 27: Databinding trong Android
- Bài 28: Toolbar, ActionBar trong lập trình Android
- Bài 29: AsyncTask – thread & handler trong Android
- Bài 30: Các thư viện thường dùng trong Android
- Bài 31: Tìm hiểu về MVC, MVP và MVVM
- Bài 32: AlarmManager trong Android
- Bài 33: Permission trong Android
- Bài 34: Đóng gói ứng dụng Android